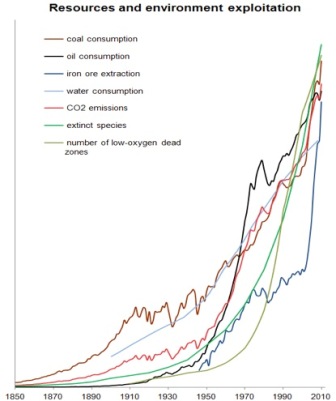
Put simply, any generation of economic value requires resources. These resources are extracted from somewhere in the world, used in some fashion to create energy or further materialsUnfortunately, there are fundamental flaws in this plan. The Energy Return on Investment (EROI) of renewable energies is generally much lower than that of fossil fuels. In other words, for a given amount of resources invested in renewables, you receive much less usable energy back than the same investment in fossil fuels would yield. This is because power such as that from the sun and wind is more diffuse and harder to capture. Renewables, therefore, require more land, and their construction is energy-intensive and necessitates many rare earth materials. So although renewables create fewer carbon emissions than fossil fuels, their ecological impact shifts into other forms. Accordingly, recent research has shown that absolute decoupling of economic growth from material impact is incredibly unlikely, especially at the scale and pace needed to limit global warming to below the much-discussed two-degree rise above pre-industrial levels. Even if a global rollout of renewable technologies occurred tomorrow, it is unlikely that their energy returns would be sufficient to meet the current energy demand of the global economy. For these reasons, the growth paradigm cannot deliver the economic and social transformation required to meaningfully combat climate and ecological breakdown. If we are to create a just and sustainable future for life on Earth, we must instead look to alternative economic paradigms which explicitly contest the growth imperative. One such paradigm is degrowth.
Degrowth does not represent the opposite of growth, recession, but a complete restructuring of society around values of conviviality, solidarity, and sufficiency.To achieve this aim, degrowth argues for establishing more localized economies, which reduce the reliance on high-emission international trade flows. By strengthening the role of co-operatives, solidarity and sharing economies, production processes could be democratically organized around social and ecological well-being, rather than the resource-insatiable profit motive. As a result, the power of the wage-labour market over peoples’ lives would also be diminished. Consequently, degrowth not only provides a practical route out of climate breakdown but also offers the prospect of simpler, more fulfilling ways of living, where more time can be dedicated to community, relationships and creative pursuits. To reframe Kennedy’s words, degrowth truly has the power to prioritize the things which make life worthwhile.

In his welcome address at the opening plenary of the 5th International Degrowth Conference, Federico Demaria from Research and Degrowth made explicitly clear that immigrants, refugees and their struggles must be integral part of the degrowth community: "Refugees and the other oppressed shall always be kept in mind while imagining degrowth and the socio-ecological transformation we are walking. ...
By Nafeez Ahmed New research suggests that the ongoing global economic crisis is symptomatic of a deeper crisis of industrial civilization’s relationship with nature. The continuation of the crisis, though, does not imply the end of the world – but rather is part of major phase shift to a new form of civilization that could either adapt to post-carbon reality and prosper, or crumble in denial....

If current crises like environmental degradation and social inequality can be seen as result of our economic and social systems, the concept of a degrowth economy has been advanced as a possible solution. Degrowth is in direct contrast to economic systems such as capitalism or sustainable growth, and in fact has much more in common [...]