In the face of unfettered globalization, the rise of right-wing movements around the globe and the dangers of climate catastrophe, it seems easier to imagine the end of the world than an end to capitalism, growth and domination. However, in recent years something new has emerged to counter what Mark Fisher has called “capitalist realism:” after decades on the defensive against neoliberalism, the left has once again started to embrace positive visions of the future. This can be seen in the movements behind the rise of Jeremy Corbyn and Bernie Sanders, for example, but also in a new wave of prefigurative social movements ranging from community gardens and worker-owned co-ops to the Women’s Protection Units (YPJ) in Rojava and the “transformative economies” highlighted by the 2019-20 World Social Forum in Barcelona – new economic models and practices around the commons, agroecology and cooperatives aimed at transforming the existing economic system. All these are movements that “embody their ultimate goals and their vision of a future society through their ongoing social practices, social relations, decision-making philosophy and culture.” These progressive visions fall into two broad camps, most clearly symbolized by the eco-modernist notion of “fully automated luxury communism” on the one hand, and “degrowth” on the other. While sharing an understanding of the need for systemic alternatives and a critique of domination, the split between these perspectives and the social movements associated with them runs deep. As argued by world system theorist Immanuel Wallerstein, not only are the world’s economic and political elites divided between globalists and authoritarians, there is also a split within the left, between the ‘progressive productivists’ who - in the tradition of the socialist and social democratic labor movement - focus on growth, productivity gains and redistribution and tend to prefer vertical forms of organization; and those movements that, closer to the tradition of anarchism, rely on self-organization from the bottom up and fundamentally question economic growth. The new narratives of progressive productivism - best represented by Paul Mason’s “Postcapitalism” and the concept of “fully automated luxury communism” - embrace modernity, globalization and technological progress, since, they argue, these create the conditions for liberation. This strand of socialist futurism tends to ignore ecological questions and issues of global social justice (including climate justice), and flatly dismisses movements that promote localism, luddism or sufficiency as “primitivist romanticism.” Leigh Phillips, for example, condems degrowth as “austerity ecology” and criticizes the movements that promote it as “collapse-porn addicts.” For their part, the growth-critical, bottom-up prefigurative movements which seek social-ecological transformation argue that relying on technological innovation and global markets to solve humanity’s challenges is a dangerous illusion. Proponents of degrowth claim that the eco-modernist position cannot provide an answer to the most important challenge of the twenty-first century, i.e. how can we live well without externalizing the costs onto others, the planet and future generations? Answers to that question can only be found if early-industrialized countries find ways to transcend expansionary modernity. Rather than relying on techno-fixes we need to find pathways towards post-growth or degrowth societies.
• An orientation towards concrete needs and a good life for all, replacing economic concepts, abstract production figures or the rules of market exchange
• Humans as complex, relational beings: people are not seen as rational utility maximizers but as social and emotional beings living in relationship with, and depending on, each other.
• A comprehensive analysis of society, power and politics, taking into account the many different facets of existing inequalities and crises.
• Global justice instead of only discussing political questions in a national context.
• Rejection of the ‘green economy': multiple crises can’t be solved through a ‘greening’ of growth and capitalism; large-scale technological solutions have major, negative side-effects.
• Democratization: instead of delegating the power to shape society to a selected few, most movements strive for an all-encompassing democratization that ensures the participation of all people.
• Systemic change and paradigm shift: instead of hoping that small changes or political reforms will solve society’s problems, these movements seek to bring about comprehensive and fundamental changes.
• Working in the here and now: instead of simply making demands, most movements try to effect change in the present, either through alternative projects in which utopias are tested out or in social struggles with concrete goals.
These commonalities can be the cornerstones of a common framework for an emerging alliance of progressive forces that brings together growth-critical, bottom-up, prefigurative movements – a ‘mosaic’ of alternatives.
COVID-19 is both one and the same as any other ecological crisis (such as climate change) because its emergence is rooted in the same mode of production that has generated all other ecological crises and social inequalities of our times. In late 2019, a novel coronavirus (SARS CoV-2) emerged from a wet market in Wuhan in the province of Hubei in China. It has so far resulted in cases ov...

Introducing a series of proposals for a truly transformative GND The Green New Deal is on everyone’s lips and policy platforms. Liberal pundit Thomas Friedman coined the term in 2007, and Left parties in the UK called for a Green New Deal during the recession that followed the 2008 global financial crash. Last year, Congresswoman Alexandria Ocasio Cortez rebooted the idea in the United Sta...
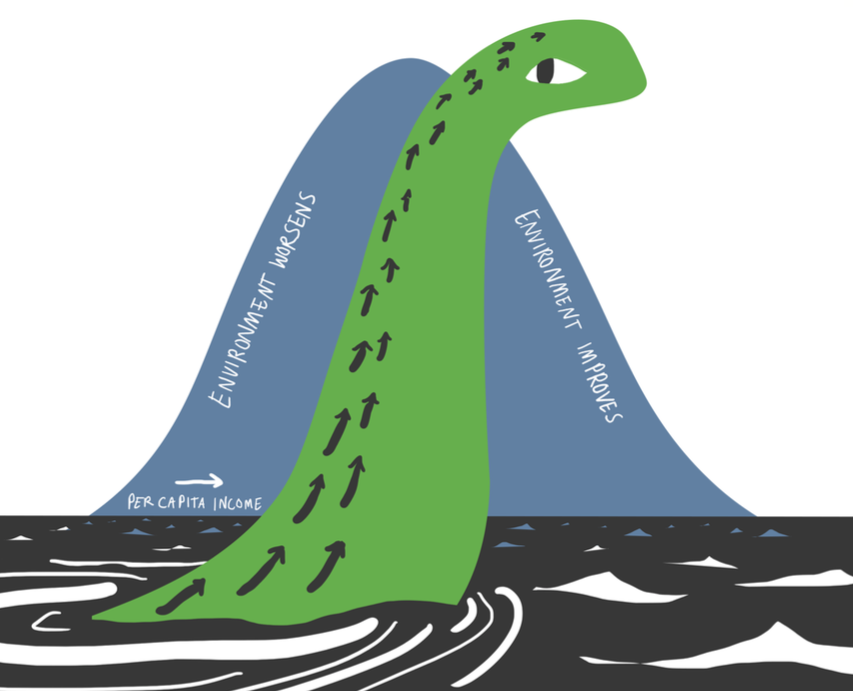
If making the degrowth case was like baking a cake, disproving the plausibility of green growth would be the equivalent of turning the oven on. Decoupling is only “a myth” or “a fantasy,” some would say, a notorious fallacy that requires as much attention as the confabulations of Flat Earthers. And yet, faith in decoupling is strengthening in environmental agendas all around the world, includin...