Read the full version of the open letter here
The current economic downturn is not Degrowth, even if some people misleadingly call it that. Degrowth means ensuring everybody's basic needs are met by transforming our societies. With policies in place to do that, we could shut down much of the economy for months and everyone would still have enough food, shelter, and healthcare. In a Degrowth society, with relocalized economies, a pandemic like COVID-19 would be less likely, would spread less, and would cause less suffering. The economic crisis triggered by the pandemic is related to our dependence on growth. All interested individuals and organizations are invited to engage in an open debate to re-envision economy and society in the wake of the corona crisis. From May 29 to June 1, the (now online) international conference “Degrowth Vienna 2020: Strategies for a Social Ecological Transformation” will be held, and the Global Degrowth Day on June 6th.Catalan Croatian Danish Dutch French German Greek Hungarian Italian Korean Mandarin Portuguese Russian Slovenian Spanish Swedish Turkish

Technological pipe dreams and the fixation on perpetual growth have prevented effective climate policies for decades "Happiness does not pay pensions", said the Austrian chancellor Sebastian Kurz at the recent World Economic Forum in Davos. The statement aimed to criticize the idea of a “post-growth” or “degrowth” society, which has received increasing attention in light of the climate crisis....
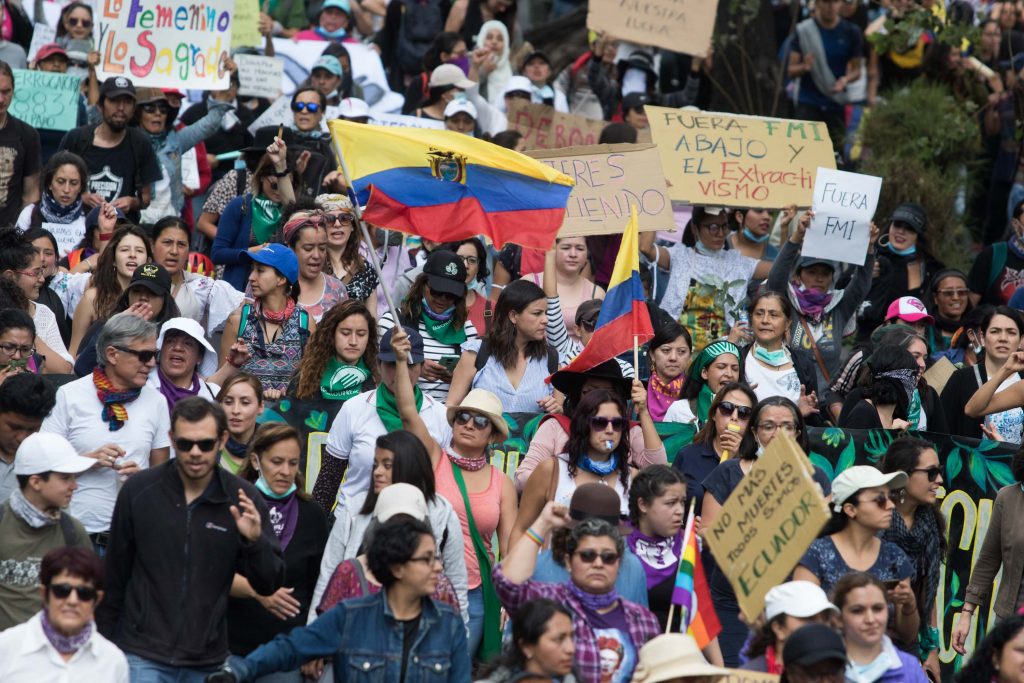
On October 1st, Ecuadorian President Lenin Moreno announced a series of economic measures for the country, including the elimination of gasoline and diesel subsidies and the liberalization of their prices, as part of an agreement with the International Monetary Fund (IMF). These measures led to the eruption of massive nationwide protests for eleven consecutive days, which were met by the govern...

Australia’s two-speed economy, in which those engaged in mineral extraction flourish while the rest flounder, seems to have only one direction: up. Not that people really stop to think why. Most Australians, if you asked them, would stare blankly if you mentioned degrowth, or crack a joke about how it’s tantamount to devolution. It seems [...]